By just making the users visiting a link, an attacker can hack the users’ iOS/macOS Camera using zero-day bugs in Safari.
With iOS and macOS camera security model every app needs to assigned permission manually but Apple’s own app such as Safari gets access by default.
Security researcher Ryan Pickren discovered seven new vulnerabilities with Safari browser that allows attackers to access your device’s camera, microphone, or location, and in some cases, saved passwords as well.

Pickren said that Safari not using the method of the origin to keep track of the open website, “I deduced that Safari was likely running a Generic URI Syntax parser against all open windows to get the URIs’ hostnames, then doing some extra parsing on those.”
Exploiting Bugs to Access Camera
He started exploiting using javascript: data: and about, but that fails, but while parsing file: which specified for remote or FTP purpose(file://host.example.com/Share/path/to/file.txt).
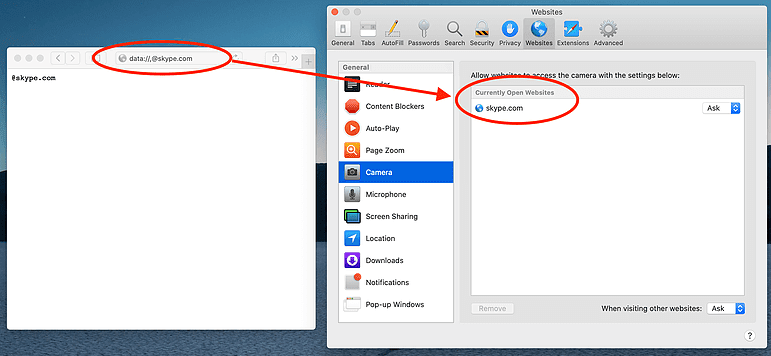
Safari parses it as a normal file URI, “the page actually accepted this URI as valid and reloaded the same content. Which means I just changed the document.domain using this really dumb trick. (CVE-2020-3885).”
So now the Safari browser thinks the website connected is skype9.0com, by opening the local file attackers can run a malicious script and gain access to Camera, Microphone, and Screen Sharing.
He found another bug (CVE-2020-9784 & CVE-2020-3887) to bypass the auto-download prevention in the Safari browser.
By using blob://skype.com URI a popup can be triggered and can be used to execute the arbitrary JavaScript.
Trying all chain of bugs can grant access to iOS/macOS camera, microphone, or location, and in some cases, saved passwords.
Following are the seven bugs
CVE-2020-3852 – A logic issue was addressed with improved validation.
CVE-2020-3864 – A DOM object context may not have had a unique security origin
CVE-2020-3865 – A top-level DOM object context may have incorrectly been considered secure
CVE-2020-3885 – File URL processed incorrectly.
CVE-2020-3887 – A download’s origin may be incorrectly associated
CVE-2020-9784 – Malicious iframe use another website’s download settings
CVE-2020-9787 – Hostnames with a dash (-) and period (.) are ignored

All the vulnerabilities patched in January and March updates. The researcher receives $75,000 for the bug submission.



.png
)

