The Apache ActiveMQ server is vulnerable to remote code execution (CVE-2023-46604), where attackers can exploit this vulnerability by manipulating serialized class types in the OpenWire protocol to load malicious class configurations from external sources.
Successful exploitation allows attackers to execute arbitrary code on the vulnerable server, leading to potential system compromise, which has been actively exploited by various threat actors, including Andariel, HelloKitty, and Cobalt Strike, highlighting the critical need for prompt patching.
CoinMiner attackers exploited a vulnerability in Apache ActiveMQ servers to install Frpc malware, which allowed threat actors to execute commands remotely, potentially leading to further compromises.
Leveraging 2024 MITRE ATT&CK Results for SME & MSP Cybersecurity Leaders – Attend Free Webinar
The attack involved downloading and executing malicious XML configuration files from a remote server, which were then loaded by the vulnerable ActiveMQ process.
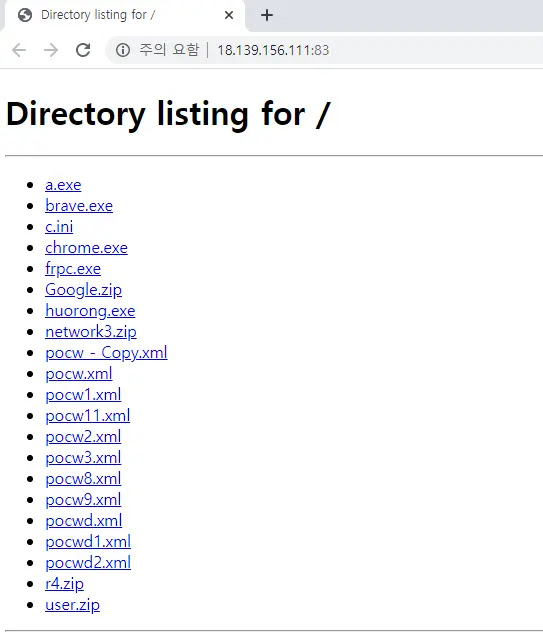
The attacker leverages an ActiveMQ vulnerability to execute commands that add a backdoor account named “adminCaloX1” with administrative privileges and enable remote desktop access (RDP).
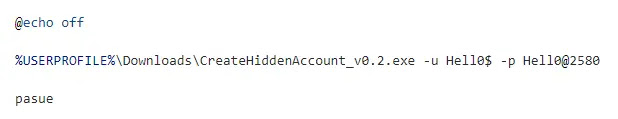
They utilize a combination of PowerShell cmdlets and the open-source tool “CreateHiddenAccount” to achieve this, which likely originates from a Chinese source, further suggesting the attacker’s potential background.
It is possible that the attacker is attempting to facilitate RDP access within a private network with the download and execution of Frpc.
Quasar RAT, a .NET-based open-source RAT, provides comprehensive remote access capabilities by enabling threat actors to execute commands, manipulate files and registry entries, and steal sensitive information through keylogging and account harvesting.
It also facilitates real-time system control via remote desktop, as this specific instance of Quasar RAT leverages a C&C server located at 18.139.156[.]111:4782, suggesting a dual-pronged attack approach combining remote desktop control and stealthy RAT operations.
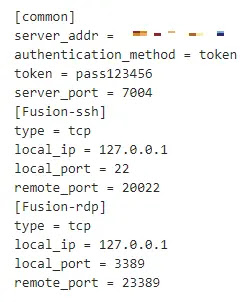
The threat actor leveraged the ActiveMQ vulnerability to deploy Frpc, a reverse proxy tool, onto compromised systems, which was facilitated by a PowerShell command.
The primary objective of Frpc is to establish a connection between a specific port on the infected system (port 3389 in this case) and an external relay server, which likely another compromised system located in Korea, allows the threat actor to remotely access the infected system via RDP, bypassing potential network restrictions.
According to ASEC, Mauri ransomware, an open-source tool, is being weaponized by threat actors. Despite being initially intended for research, its public availability has enabled malicious use.

The ransomware encrypts various file extensions using AES-256 CTR and demands a ransom in USDT. While the current C&C server is localhost, indicating potential testing, the modified configuration suggests active exploitation.
Apache ActiveMQ versions 5.18.0-5.18.2, 5.17.0-5.17.5, 5.16.0-5.16.6, 5.15.15 and earlier, and Legacy OpenWire Module versions 5.18.0-5.18.2, 5.17.0-5.17.5, 5.16.0-5.16.6, and 5.8.0-5.15.15 are vulnerable to attacks.
Threat actors exploit these vulnerabilities to install CoinMiners, malware, or ransomware. To mitigate risks, system administrators must update to the latest versions, implement firewalls, and update V3 to the latest version to prevent malware infections.
Analyse Real-World Malware & Phishing Attacks With ANY.RUN - Get up to 3 Free Licenses



.png
)
