A critical security flaw dubbed “Media File Jacking” affected WhatsApp and Telegram for Android let hackers manipulate both apps media files if users enable certain features.
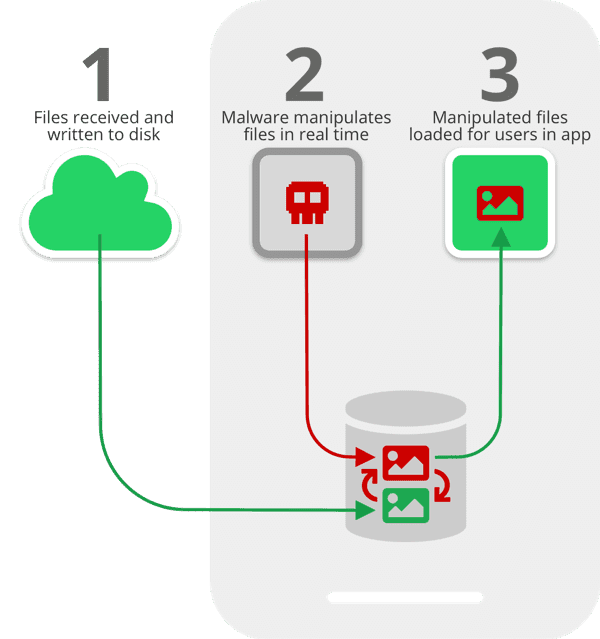
Threat actors are able to intercept and manipulate media file without the user’s knowledge when a pause in continuity in-between time when media files received through the apps that are written to the disk and user loaded media in the apps chat user interface (UI).
Successful exploitation of this critical vulnerability presented in WhatsApp and Telegram let attackers manipulate the sensitive information and misuse the user’s photos and videos, corporate documents, invoices, and voice records.
Researchers demonstrate that the Media File Jacking vulnerability let attackers to successfully manipulate media files by taking advantage of logical flaws in the apps.
Media File Jacking – Technical Explanation
There are two types of storage location (internal and external storage) used by Android apps to store media files and data.
When users stored the files in internal storage can be accessed only by the respective app which means that other apps can’t access those files.
But, the files saved to an external storage public directory are world-readable/writeable can be accessed by other apps or users which actually beyond the app control.
In WhatsApp, files are stored in external storage by default (/storage/emulated/0/WhatsApp/Media/) similarly Telegram stored in same external storage (/storage/emulated/0/Telegram/ ).
So both apps load the received files from the public directories for users to see in the chat interface which leads to a critical security risk for the integrity of the media files.
According to Symantec Research, Write-to-external storage (WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE) is a common permission requested by Android apps, with over a million apps in Google Play having this access. In fact, based on our internal app data, we found nearly 50% of a given device’s apps have this permission.
During their research, the attacker performs the exploitation with the help of malware that can instantaneously analyze and manipulate the files and gain access.
The manipulation process takes place between, when files are first received on a device and written to the disk ( Image 1) and when they are loaded for users to consume via the apps (Image 3)
Some of the following scenarios where attackers could exploit this vulnerability.
Attackers Manipulating the Victims Data
1. Image manipulation
In this scenario, a malicious application that posed as a legitimate app downloaded by a user can manipulate personal photos in near-real time without letting know the victims.
This malicious app silently running in the background and performs a Media File Jacking attack while the victim uses WhatsApp
You could see that it monitors for photos received through the IM app, identify faces in the photos, and replaces them with something else and modifies the real face.
2. Payment manipulation
In this attack, threat actors manipulate the invoice sent by the vendor to the customer in transit and alter the payment details to transfer the amount to the attacker’s bank account, but the customer has no knowledge that it’s been altered.
3. Audio Message Spoofing
In this attack, hackers using deep learning technology to alters the original audio file to communicate to the CFO, in the CEO’s own voice, that a payment needs to be transferred immediately to a fictitious party, which is in fact the attacker.
In this case, the original message from the CEO is replaced when it arrives at the CFO’s phone.
Fake New Media File Jacking
In Telegram, Admins creating a channel to broadcast the messages to an unlimited number of subscribers. Here, an attacker can manipulate the media files that were shared within the channel without the knowledge and consent of both the channel owner and the end-victim.
How to Protect from Media File Jacking Attack
Whats and Telegram Users can Disable the feature that saves media files to external storage will prevent the risk of Media File Jacking.
WhatsApp: Settings -> Chats -> Media Visibility -> Disable
Telegram: Settings -> Chat Settings -> Save to Gallery -> Disable
You can follow us on Linkedin, Twitter, Facebook for daily Cybersecurity updates also you can take the Best Cybersecurity course online to keep yourself updated.
Also Read:
WhatsApp Hacked – Attackers Exploit iPhone or Android device by Making a WhatsApp call



.png
)