The Roaming Mantis threat group distributes a well-known Android malware family called “MoqHao.” This malware family has been previously reported to be targeting Asian countries such as Korea and Japan. Though the distribution method remains the same, the new variants use a very dangerous technique.
Typically, the MoqHao malware requires user interaction to install and launch the app. However, the new variant of this malware does not require any execution.
Android is currently protected with Google Play Protect, which is the default app scanner that warns users or blocks applications that contain malicious behavior.
Perimeter’s 81 Malware Protection for Network Based Threats
Prevent malware from infecting your network at the delivery stage by intercepting malicious files in transit from their source to the target device’s web browser. .
Android MoqHao Malware
As part of the distribution, the threat actors send a malicious phishing SMS message to the users, which will contain a malicious shortened link. The device downloads the malicious application once the user clicks on the link.
This new variant has several different behaviors when compared to the previous variants of this malware, as it launches automatically after installation without user interaction.
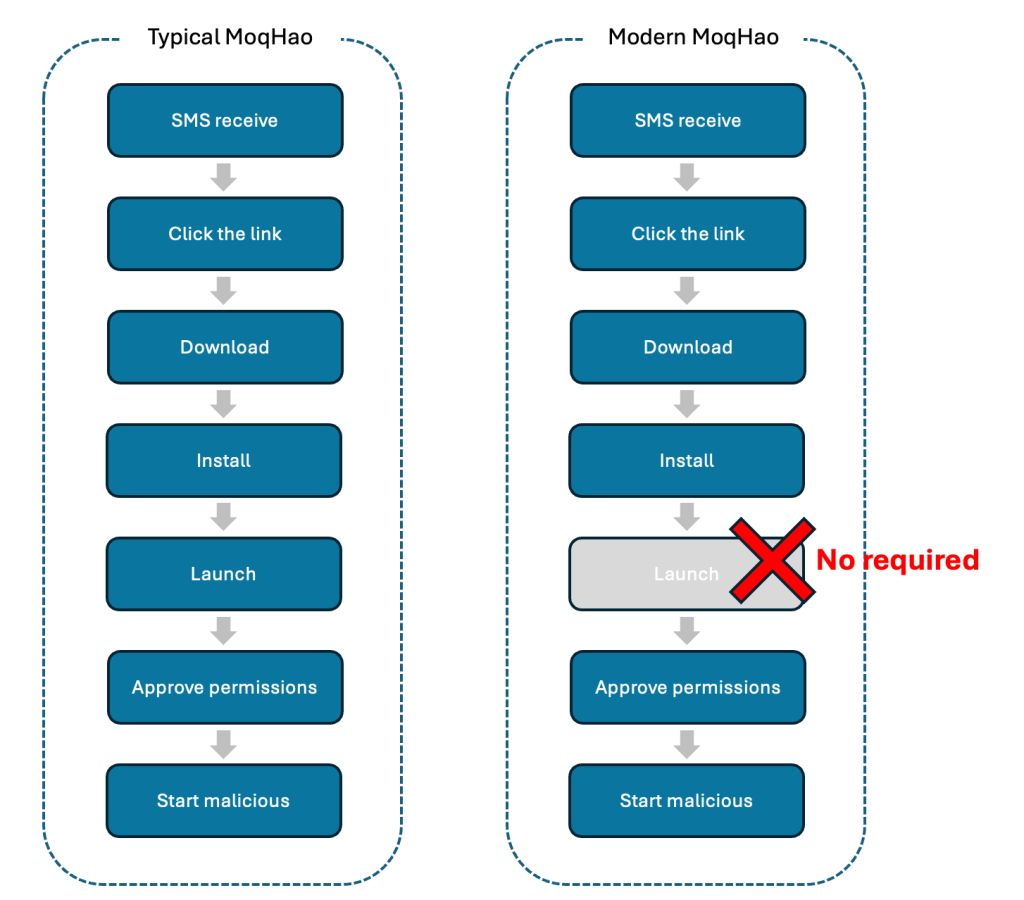
Android security checks an installed application and the specific value used by that application, which must be unique. The threat actors are abusing this particular feature to auto-executing the application without user interaction.
Moreover, the threat actors also use social engineering techniques to set this malicious app as a default SMS app. Further investigations also revealed that the malware has been extended with targets, including countries like South Korea, France, Germany, and India.
Furthermore, this variant connects with a C2 server through WebSocket. This new malware has been added with several other commands for checking SIM state, sending SMS messages to other contacts and C2 servers, setting Sound/Vibrate/Silent mode, and various other purposes.
| Command | Description |
| getSmsKW | Send whole contacts to the C2 server |
| sendSms | Send SMS messages to someone |
| setWifi | Enable/disable Wifi |
| gcont | Set Vibrate/Silent mode according to the SDK version |
| lock | Store Boolean value in “lock” key in SharedPreferences |
| bc | Check SIM state |
| setForward | Store String value in “fs” key in SharedPreferences |
| getForward | Get String value in “fs” key in SharedPreferences |
| hasPkg | Check the specific package installed on the device |
| setRingerMode | Set Sound/Vibrate/Silent mode |
| setRecEnable | Emulate the Home button click |
| reqState | Send device information (Network, Power, MAC, Permission) to C2 server |
| showHome | Call a specific number with a Silent mode |
| getnpki | Send Korean Public Certificate (NPKI) to C2 server |
| http | Send HTTP requests |
| call | Get the list of installed packages |
| get_apps | Send all photos to the C2 server |
| ping | Check C2 server status |
| getPhoneState | Get unique information such as IMEI, SIM number, Android ID, and serial number |
| get_photo | Send all photos to C2 server |
McAfee provides comprehensive information about the malware, including details on its source code, techniques used to deploy it, targets that have been affected by it, and other important insights.
Indicators of Compromise
| SHA256 | Application Name | Package Name |
| 2576a166d3b18eafc2e35a7de3e5549419d10ce62e0eeb24bad5a1daaa257528 | chrome | gb.pi.xcxr.xd |
| 61b4cca67762a4cf31209056ea17b6fb212e175ca330015d804122ee6481688e | chrome | malmkb.zdbd.ivakf.lrhrgf |
| b044804cf731cd7dd79000b7c6abce7b642402b275c1eb25712607fc1e5e3d2b | chrome | vfqhqd.msk.xux.njs |
| bf102125a6fca5e96aed855b45bbed9aa0bc964198ce207f2e63a71487ad793a | chrome | hohoj.vlcwu.lm.ext |
| e72f46f15e50ce7cee5c4c0c5a5277e8be4bb3dd23d08ea79e1deacb8f004136 | chrome | enech.hg.rrfy.wrlpp |
| f6323f8d8cfa4b5053c65f8c1862a8e6844b35b260f61735b3cf8d19990fef42 | chrome | gqjoyp.cixq.zbh.llr |
Stay updated on Cybersecurity news, Whitepapers, and Infographics. Follow us on LinkedIn & Twitter.



.png
)
