Researchers discovered a new PureLocker Ransomware that capable of encrypting files in Windows, Linux, and macOS. The ransomware used by threat actors to perform a targeted attack against production servers of the enterprise networks.
Code reuse analysis against Purelocker reveals that the ransomware related to the “more_eggs”, a backdoor malware often used by Cobalt Gang, FIN6 threat actors and is sold in the dark web.
The ransomware is written in the PureBasic programming language and it is very difficult for AV vendor to write a signature for PureBasic binaries and is portable between Windows, Linux, and OS-X.
PureLocker Ransomware mainly targeting both Windows and Linux infrastructure and the attackers using a lot more evasion techniques to fly under the radar and undetected the ransomware for several months.
PureLocker distributed as a Ransomware-as-a-Service Being Used in Targeted Attacks Against Enterprise Servers.
PureLocker Sample Analysis
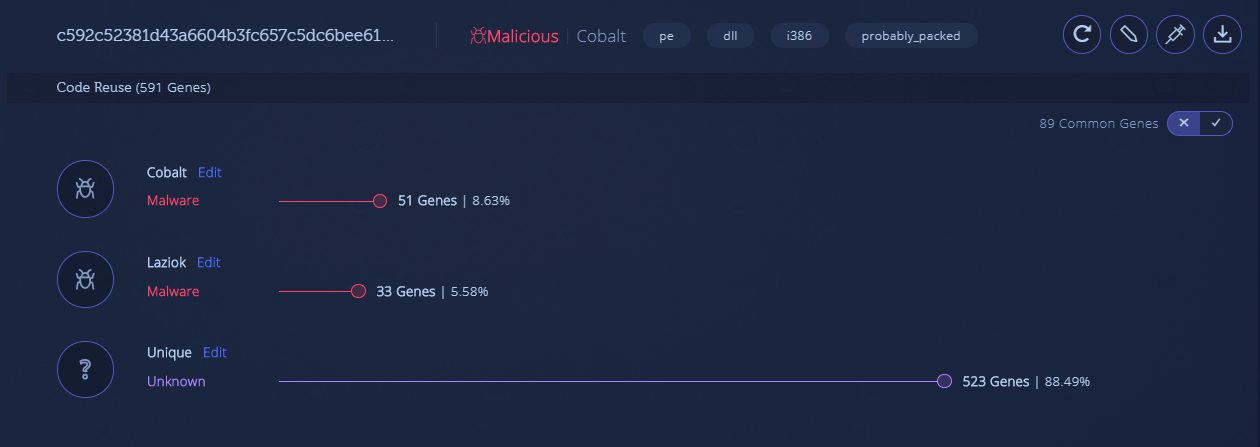
A ransomware sample that compatible with Windows that posed as C++ cryptography library called Crypto++ and the researchers digging deeper and analyzed the sample and find the following keys.
1.There is no Crypto++ code connection here, meaning the sample is not a Crypto++ library.
2. The file contains reused code from several malware families, mainly from Cobalt Gang binaries. This means the file is malicious and may have relations to Cobalt Gang.
3. The majority of the relevant code in this file is unique, indicating that it’s likely a new or highly modified malware.
During the infection, the malware code starts checking to ensure that the file executed as expected by malware authors and the malware exit if it fails any one of these checks.
Once the malware executes its payload, then it deletes itself and also using the anti-analysis technique will never let rise suspicion.
According to Intezer research, In the event that all anti-analysis and integrity tests performed by the malware are satisfied, it proceeds to encrypt the files on the victim’s machine with the standard AES+RSA combination, using a hard-coded RSA key.
After it completes the encryption process, The ransomware adds the “.CR1” extension for each encrypted file and delete the original file to prevent the recovery.
Later the Purelocker drops the ransom note file on the user’s desktop named YOUR_FILES(.)txt.
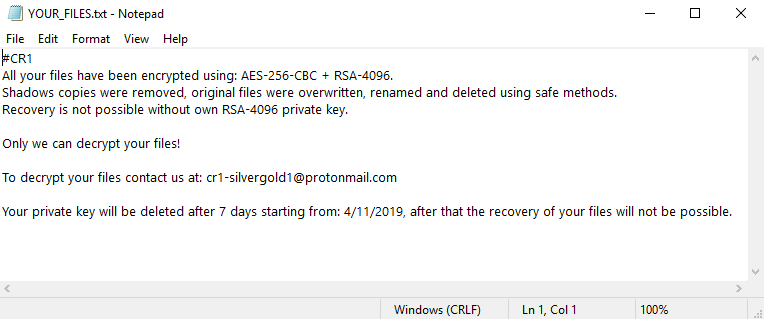
Ransom note doesn’t contain any payment information, instead, attacker request users to contact via email. for that, they are using anonymous and encrypted Proton email service.
“Since this is a RaaS, we believe this string is most likely the identifier of the group that is operating these specific samples,” Intezer said.
You can also read the complete Ransomware Attack Response and Mitigation Checklist.
You can follow us on Linkedin, Twitter, Facebook for daily Cybersecurity and hacking news updates.



.png
)
