Researchers discovered seven malicious apps from the Google Play store that drops malware and adware on Android users and opens backdoor access to the attackers.
These apps are installed by over 11,000 Android users from Google Play.
These apps perform various malicious activities including draining device batteries and consuming excessive amounts of mobile data.
Mobile malware is continuously increasing and the threat actors always finding new ways to bypass security features in Google Play by deploying various tactics and techniques to target the millions of Android users around the world.
3 Different developers have uploaded the following malicious apps to the Google play store.
- PumpApp (Developer) – Magnifying Glass, Super Bright LED Flashlight
- LizotMitis (Developer) – Magnifier, Magnifying Glass with Flashlight, Super-bright Flashlight
- iSoft LLC (Developer) – Alarm Clock, Calculator, Free Magnifying Glass
“The dropper apps are designed to download and install APKs from a GitHub repository, essentially opening a backdoor on the device for any new application functionality to be installed.”
Malware droppers are carefully handling the communication with GitHub and waiting for the initial setup for evading detection by security researchers and malware detection agents.
GitHub URL is embedded within the Dropper App code and it is completely obfuscated to avoid flagging by human analysis and escape from Google Play protect scan.
Download the Adware APK
Researchers uncovered the configuration data for the dropper app and additional URLs from the obfuscated JSON message and it pointed to the Adware APK.
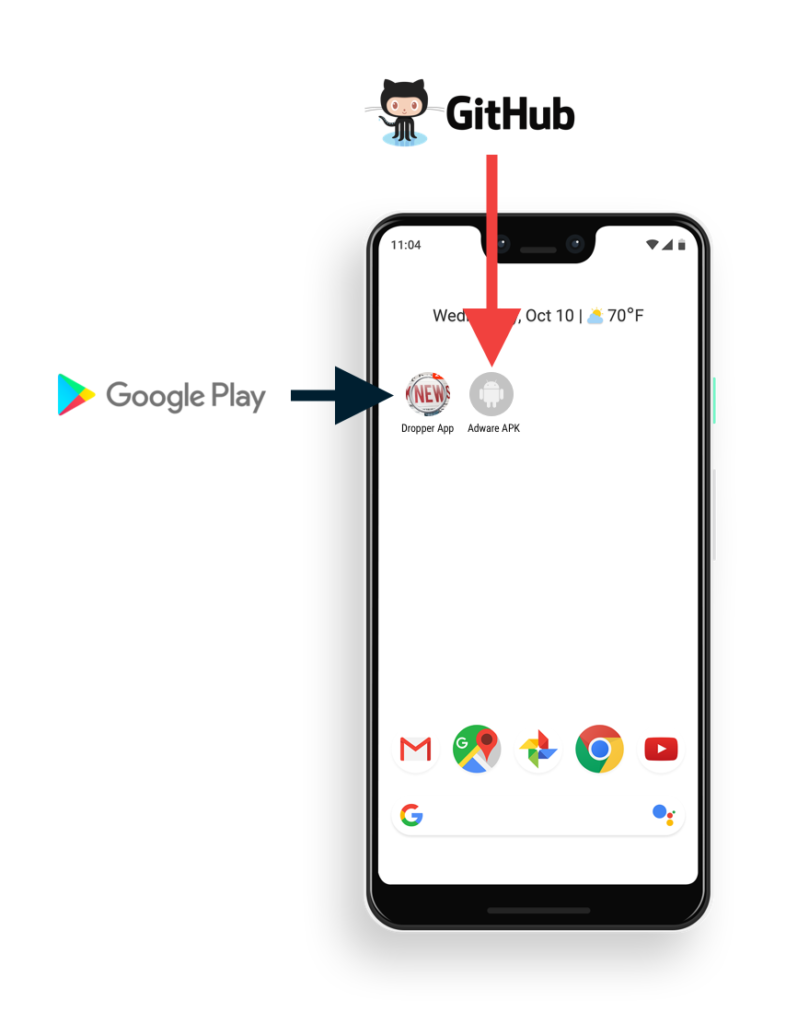
After the installation of the malicious dropper apps, the adware APK will be triggered and wait for 10 min before starting its malicious activities.
The App aggressively shows fullscreen video ads, outside of the app, without any user interaction and the app is capable of performing overlaying other applications to display the Ads anytime once the user’s Android device gets unlocked.
According to Wandera’s research, If the screen is turned off and no passcode is set up, the adware activates the ad in set intervals, turns on the screen, and plays the video ads until the user realizes and closes them.
But if the user’s device is protected with a password, it won’t bypass the passcode but it simply turns on the screen and run the video ads in the background which causes CPU spikes and battery consumption.
Only manual dismissal is an option to stop the ad because the adware can self-execute without user interaction and it’s continuously running the video ads without user attention when the mobile is kept in the bag or packet.
These apps also violate the following Google policy,
“An app distributed via Google Play may not modify, replace, or update itself using any method other than Google Play’s update mechanism. Likewise, an app may not download executable code (e.g. dex, JAR, .so files) from a source other than Google Play.”
Recommend that users with these apps installed find both the dropper apps and payload apps and uninstall them manually from the device.
Recently Google tied up with mobile security companies to find bad apps before it reaches the user’s device. The primary goal of the alliance is to make Google Play more secure.
You can follow us on Linkedin, Twitter, and Facebook for daily Cybersecurity and hacking news updates.



.png
)
