In a groundbreaking discovery on November 20, 2024, cybersecurity researchers Shubham Shah and a colleague unearthed a major security vulnerability in Subaru’s STARLINK connected vehicle service.
The flaw allowed unauthorized, unrestricted access to vehicles and customer accounts across the United States, Canada, and Japan.
By exploiting this vulnerability, malicious actors could remotely control vehicle functions and access sensitive customer data actions that included unlocking vehicles, tracking location history, and retrieving personally identifiable information (PII).
Subaru quickly patched the vulnerability within 24 hours after receiving the researchers’ report, averting potential large-scale exploitation.
The researchers detailed how minimal user information, such as a victim’s last name, ZIP code, email address, phone number, or license plate, was sufficient to exploit the STARLINK system.
This access allowed them to perform actions such as remotely starting, stopping, locking, and unlocking vehicles.
They also managed to retrieve a vehicle’s one-year location history, accurate to within five meters, and access customers’ sensitive data, including emergency contacts, billing information, and even vehicle PINs.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links & Phishing Attacks With Threat Intelligence Lookup - Try for Free
Systemic Flaws in Access Controls
The researchers initially examined Subaru’s MySubaru mobile app but found its security robust.
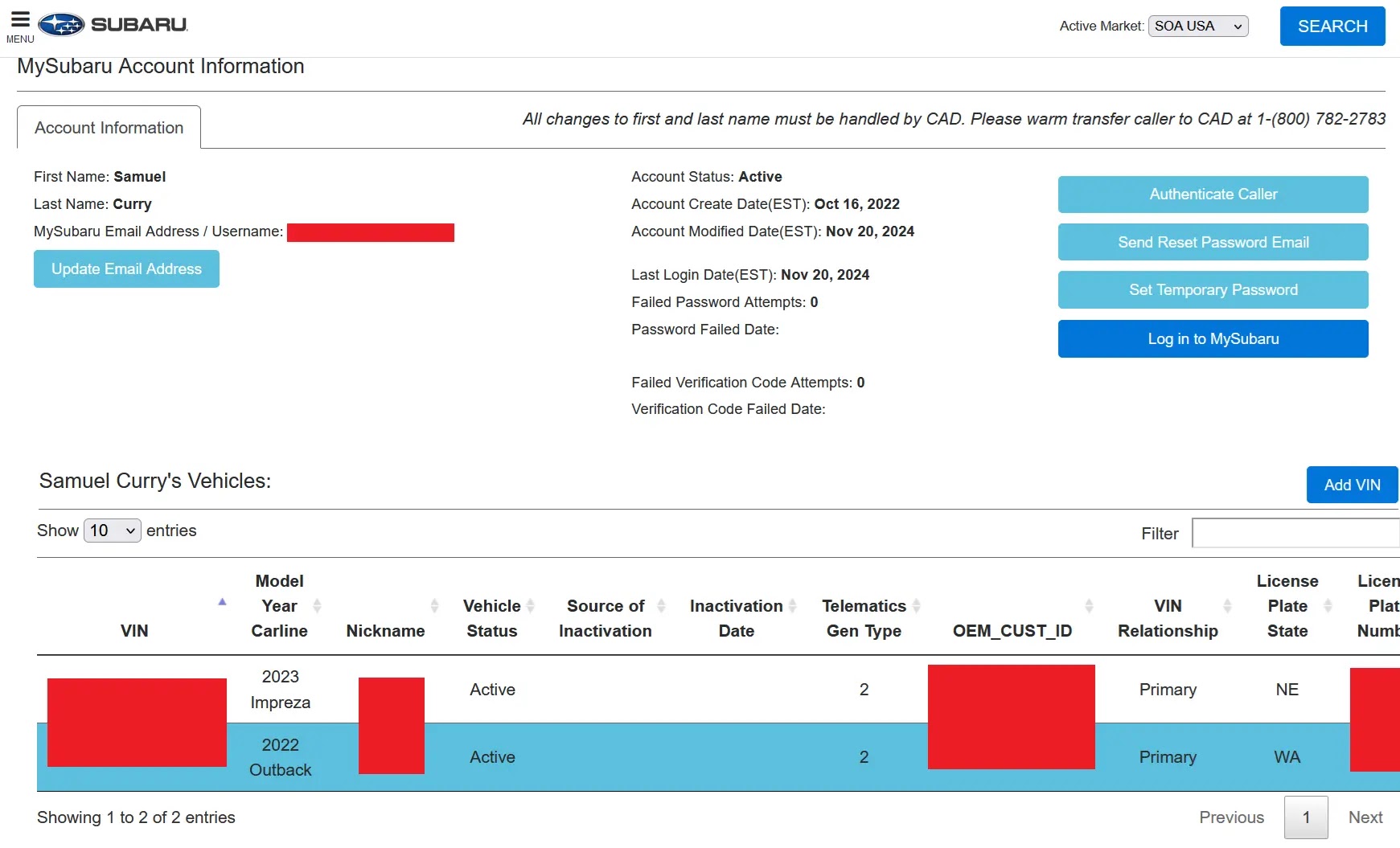
Shifting focus, they investigated Subaru’s back-end systems and stumbled upon an employee-facing STARLINK admin panel, which provided broad access to vehicles and customer records.
By exploiting a flaw in the “resetPassword.json” endpoint, they reset employee passwords without requiring verification or a token.
Using publicly available information, such as employee email addresses from LinkedIn, they successfully gained unauthorized access to the system.
Further investigation revealed the admin panel’s weak two-factor authentication (2FA) implementation, which the researchers bypassed with simple client-side modifications.
2FA bypassed.
Once inside, the admin dashboard provided unfettered access to vehicle control features and customer data for STARLINK-enabled vehicles.
Real-World Scenarios and Vehicle Access
To validate the severity of the vulnerability, the researchers conducted controlled experiments on their own vehicles and those of consenting individuals.
For example, they added themselves as authorized users to a friend’s Subaru by using the admin panel and then successfully executed remote commands, including unlocking the vehicle, all without the owner receiving any notification.

The Subaru STARLINK admin panel.
The researchers also demonstrated the ability to retrieve extensive customer information, such as physical addresses, emergency contacts, and billing data, all from the STARLINK admin dashboard.
The researchers reported the vulnerability to Subaru’s security team late on November 20, 2024.
Subaru acknowledged the flaw the next morning and deployed a fix by the afternoon, preventing further exploitation.
While the company’s swift action mitigated potential harm, the incident highlighted systemic challenges in securing connected vehicle systems.
The auto industry, as the researchers pointed out, often grants extensive access to sensitive data by default to employees, relying heavily on trust.
This discovery underscores the critical need for robust access controls, multi-layered authentication mechanisms, and rigorous security testing in connected vehicle systems.
As automation and connectivity continue to define modern vehicles, vulnerabilities like this could have far-reaching consequences for user safety and privacy.
Integrating Application Security into Your CI/CD Workflows Using Jenkins & Jira -> Free Webinar



.png
)
