In a concerning new development, cybercriminals are exploiting the widespread popularity of the recently launched DeepSeek AI chatbot to distribute the Vidar Stealer malware.
According to research by Zscaler ThreatLabz, attackers are using brand impersonation tactics to lure unsuspecting users into executing malicious code, thereby compromising sensitive data.
Launched on January 20, 2025, DeepSeek quickly gained global attention, making it a prime target for malicious campaigns.
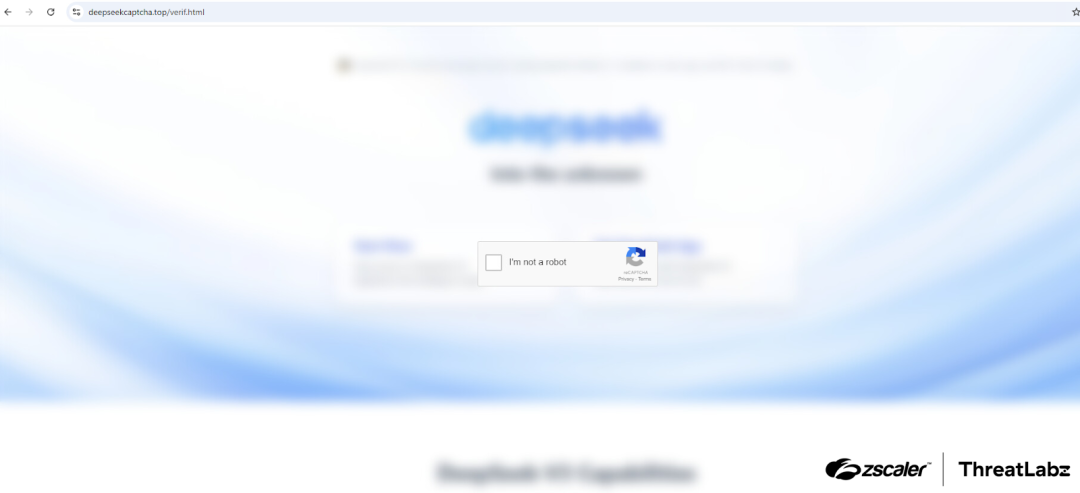
Threat actors have created fraudulent websites mimicking DeepSeek’s official platform, employing fake CAPTCHA pages as part of their attack chain.
These pages trick users into executing harmful PowerShell commands that download and deploy the Vidar information stealer.
Technical Analysis of the Attack Chain
The attack begins with the creation of fake domains resembling DeepSeek’s official site.
One such domain, “deepseekcaptcha[.]top,” prompts visitors to complete a registration process before redirecting them to a deceptive CAPTCHA page.
Embedded JavaScript in this page copies a malicious PowerShell command to the user’s clipboard.
If executed, this command downloads a packed Vidar executable (1.exe) onto the victim’s system.

Once deployed, Vidar initiates its primary function: harvesting sensitive information such as login credentials, cryptocurrency wallet data, browser cookies, and personal files.
The malware also uses legitimate platforms like Telegram and Steam to conceal its command-and-control (C2) infrastructure.
Exploitation of Cryptocurrency Wallets and Browsers
Vidar is specifically configured to target cryptocurrency wallets and browser extensions.
It scans victims’ systems for wallet-related files and configurations, exfiltrating sensitive data from popular wallets like MetaMask, BinanceChainWallet, and Trust Wallet.
Additionally, it extracts browser-related assets such as saved credentials and autofill data from browsers including Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Opera GX, and Brave.
The malware also searches for specific filenames and extensions associated with cryptocurrency wallets or private keys.
By leveraging these methods, attackers can gain access to victims’ digital assets and accounts.
Vidar uses hardcoded endpoints for exfiltration of stolen data. In this campaign, attackers utilized a publicly accessible Steam community profile and a Telegram channel to locate C2 infrastructure.
Associated IP addresses include 77.239.117[.]222 and 95.216.178[.]57.
The rapid exploitation of DeepSeek underscores the risks associated with emerging AI technologies.
While generative AI tools offer significant benefits, they also create new opportunities for cybercriminals to launch sophisticated attacks.
Organizations must adopt robust security measures to mitigate these threats, including monitoring newly registered domains and educating users about phishing tactics.
Zscaler’s cloud security platform has detected indicators related to Vidar at multiple levels, providing protection against this campaign.
However, proactive measures such as implementing zero trust frameworks and restricting unsanctioned applications remain critical in combating such threats.
As AI adoption continues to grow across industries, vigilance will be essential in safeguarding users against evolving cyber risks.
Collect Threat Intelligence on the Latest Malware and Phishing Attacks with ANY.RUN TI Lookup -> Try for free



.png
)
