A critical security flaw has been identified in the Ultimate Member plugin for WordPress, which could potentially put over 200,000 websites at risk.
The vulnerability was discovered by Christiaan Swiers and reported through the Wordfence Bug Bounty Program, earning him a bounty of $2,063.00.
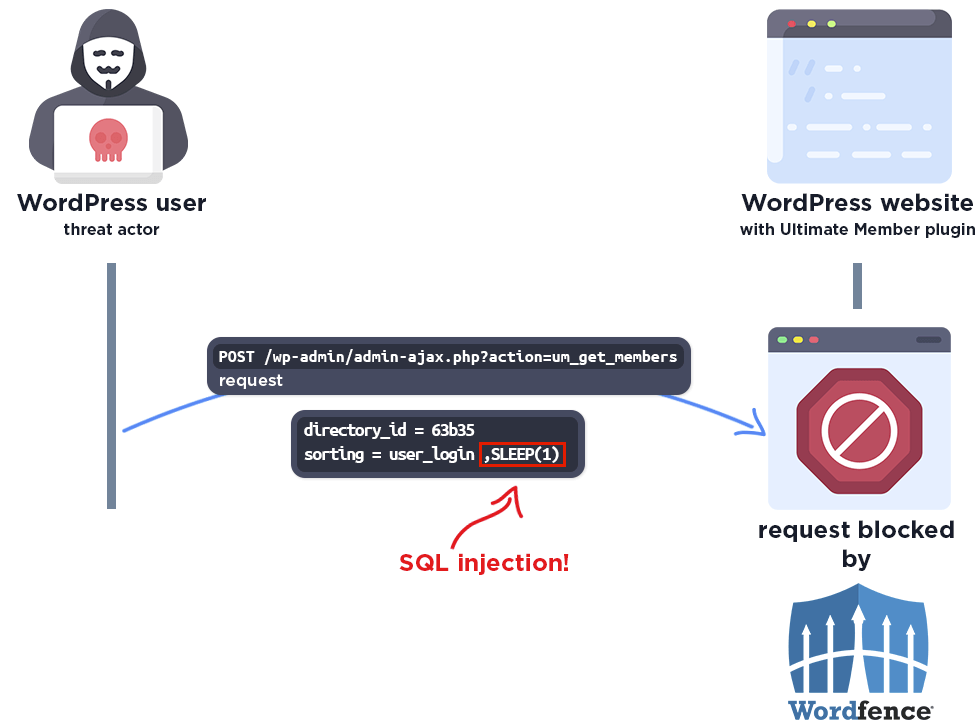
The flaw in question is an unauthenticated SQL Injection vulnerability that could allow attackers to extract sensitive data, such as password hashes, from the affected websites’ databases.
You can analyze a malware file, network, module, and registry activity with the ANY.RUN malware sandbox, and the Threat Intelligence Lookup that will let you interact with the OS directly from the browser.
Ultimate Member Plugin Flaw
The vulnerability was found in versions 2.1.3 to 2.8.2 of the Ultimate Member plugin. It was caused by insufficient escaping of the ‘sorting’ parameter and a lack of preparation in the SQL query, which could be exploited through a Time-Based blind SQL injection approach.
This method involves attackers using SQL CASE statements and the SLEEP() command to extract information based on the response time of each request.
However, it’s important to note that the vulnerability critically affects only those users who have enabled the “Enable custom table for user meta” option, as the vulnerable Member_Directory_Meta class is loaded only in this configuration.
Disclosure & Prompt Patching
Wordfence received the vulnerability submission on January 30, 2024. The same day, they validated the report, confirmed the exploit, and contacted the Ultimate Member Team.
The team responded promptly and began working on a fix after receiving full disclosure details from Wordfence.
The Ultimate Member Team released a patch on February 19, 2024, addressing the vulnerability with the updated version 2.8.3 plugin.
Wordfence urges all users of the Ultimate Member plugin to update to the latest patched version immediately to safeguard their sites against potential attacks.
You can block malware, including Trojans, ransomware, spyware, rootkits, worms, and zero-day exploits, with Perimeter81 malware protection. All are extremely harmful, can wreak havoc, and damage your network.
Stay updated on Cybersecurity news, Whitepapers, and Infographics. Follow us on LinkedIn & Twitter.



.png
)
