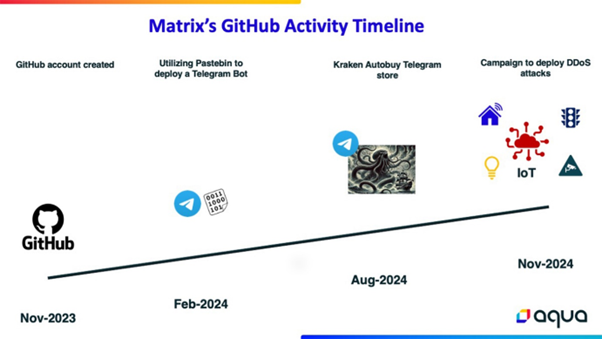
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a widespread Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) campaign attributed to a threat actor using the alias “Matrix.”
This campaign, characterized by its global scale and the actor’s low technical sophistication, highlights the evolving landscape of cyber threats where readily available tools enable even relatively inexperienced attackers to perpetrate significant attacks.
The Campaign Overview
Matrix’s operation, although not highly advanced, showcases how accessible public scripts and open-source tools can be leveraged to orchestrate large-scale cyberattacks.
The threat actor targets vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in internet-connected devices, particularly IoT and enterprise systems, using brute-force attacks and exploiting weak credentials.
Analyze cyber threats with ANYRUN's powerful sandbox. Black Friday Deals : Get up to 3 Free Licenses.
The operation builds a botnet capable of significant global disruption, utilizing compromised devices for DDoS attacks.

- Tools and Methods: Matrix employs a variety of public scripts to exploit vulnerabilities in routers, DVRs, cameras, and telecom equipment. Noteworthy vulnerabilities include CVE-2017-18368 (command injection in ZTE routers) and CVE-2021-20090 (Arcadyan firmware vulnerability).
- Targeted Devices: The primary targets are IoT devices with lightweight security, such as IP cameras, routers, and DVRs. The campaign also extends to enterprise systems, exploiting misconfigured services like Hadoop’s YARN and HugeGraph servers.
- Geographic Focus: The operation predominantly targets devices in the Asia-Pacific region, notably China and Japan, while sparing Russia and Ukraine, suggesting financial rather than geopolitical motives.
Detailed Analysis of the Infrastructure
Matrix employs a range of tools to manage and expand the botnet. An analysis of the GitHub repositories used by Matrix reveals a reliance on Python, Shell, and Golang scripts, adapted from other open-source projects.
This strategy indicates a script kiddie approach, where existing tools are customized rather than developed from scratch.
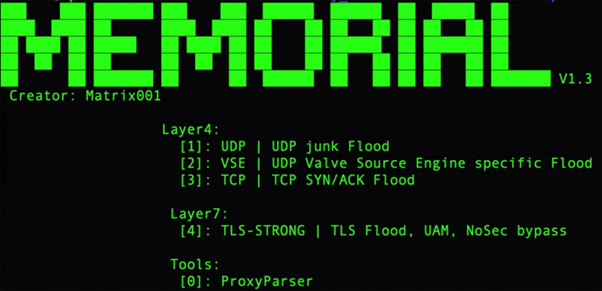
Exploited Vulnerabilities
The campaign exploits both recent and older vulnerabilities across various devices. Some of the critical vulnerabilities used include:
- CVE-2024-27348 in HugeGraph, exploited for remote code execution.
- CVE-2022-30525 and CVE-2018-10562, targeting IoT devices to ensure sustained botnet activity.
These vulnerabilities allow attackers to compromise devices, adding them to the botnet orchestrated for DDoS attacks.
The findings by Aqua Nautilus emphasize a concerning trend: the democratization of cyberattack capabilities.
With AI tools and an abundance of hacking resources, even low-skilled actors can execute sophisticated attacks. This has significant implications for cybersecurity strategies worldwide.
In response to the threat posed by actors like Matrix, organizations are urged to:
- Strengthen Default Security Settings: Change default passwords and regularly update firmware on all network-connected devices.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Isolate critical systems from IoT devices to reduce attack surfaces.
- Monitor and Respond: Use advanced threat detection systems to monitor unusual network activity and respond promptly to potential threats.
The economic impact of DDoS attacks can be substantial, affecting businesses and critical infrastructure by causing service outages.
Furthermore, devices compromised by Matrix’s botnet could be used in future attacks, amplifying the threat beyond the immediate targets.
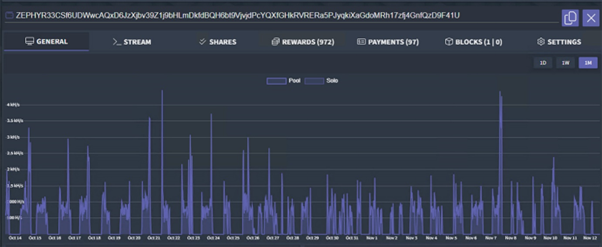
Interestingly, Matrix also conducted a cryptocurrency mining operation targeting the ZEPHYR coin, though the financial gain was minimal.
This illustrates the dual-use nature of botnets, capable of various illicit activities beyond DDoS attacks.
Matrix’s campaign serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in our connected world.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, driven by the accessibility of hacking tools and resources, both individuals and organizations must enhance their cybersecurity measures to protect against such global threats.
This campaign underscores the urgent need for robust cyber defense strategies to safeguard the digital infrastructure we increasingly rely upon.
Leveraging 2024 MITRE ATT&CK Results for SME & MSP Cybersecurity Leaders – Attend Free Webinar


