A significant evolution in the cybersecurity landscape has emerged with the uncovering of new vulnerabilities in Windows 11 (24H2).
Process Hollowing, a widely used technique often referred to as RunPE, has encountered new challenges in this operating system version due to changes in the Windows loader, impacting both security researchers and attackers alike.
Process Hollowing is a long-established process impersonation technique that allows a malicious executable to operate under the guise of a legitimate process.
Widely popular in malicious PE loaders and offensive tools, it has been a staple in the threat actor’s arsenal.
However, recent reports suggest that Windows 11 (24H2), released on October 1, 2024, has introduced disruptive changes that render many existing implementations of RunPE non-functional.
Observed Symptoms and Root Cause
The primary issue arises when a PE implant is placed into the memory of a suspended process and resumed. On Windows 11 (24H2), a critical error (0xC0000141) occurs, terminating the loading mechanism.
Investigations reveal that this stems from changes in the Windows loader related to hotpatching.
Specifically, the new function RtlpInsertOrRemoveScpCfgFunctionTable within the loading process now interacts with the ZwQueryVirtualMemory function, which executes checks on memory regions.
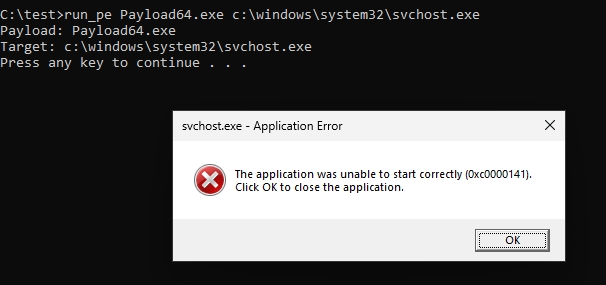
Unlike normally loaded PEs, which are stored as MEM_IMAGE, implants created via RunPE are stored as MEM_PRIVATE. This causes the ZwQueryVirtualMemory function to fail with STATUS_INVALID_ADDRESS, ultimately breaking the process.
Potential Solutions
1. Alternative Techniques
Innovators in the security field have developed hybrid techniques to circumvent the limitations of RunPE.
These methods involve mapping implants as MEM_IMAGE rather than MEM_PRIVATE, ensuring compatibility with the updated Windows loader. Some of these alternatives include:
- Process Doppelganging
- Process Ghosting
- Transacted Hollowing
- Ghostly Hollowing
- Process Overwriting
These approaches create a more legitimate-looking process and bypass the MEM_PRIVATE issue while maintaining stealth capabilities.
2. Patching NTDLL
For those still reliant on the original RunPE technique, patching the ZwQueryVirtualMemory function within NTDLL is an option.
This method involves ensuring that problematic memory queries avoid triggering errors. However, this requires careful implementation to prevent broader system instability.
These changes represent a double-edged sword. On the one hand, they enhance the resilience of Windows 11 (24H2) against classic malware techniques.
On the other hand, they challenge security testers and researchers, forcing them to adapt their tools and methods.
As Windows 11 (24H2) gains adoption, understanding and mitigating these changes is crucial for maintaining both offensive and defensive capabilities.
Are you from SOC/DFIR Teams? – Analyse Malware Files & Links with ANY.RUN Sandox -> Start Now for Free.



.png
)
