Researchers from Checkpoint found a new and previously unknown ransomware variant dubbed “Rorschach” with highly sophisticated features that target U.S. companies.
Rorschach ransomware carries technically unique and customized features and one of the fastest ransomware observed by the speed of encryption that was never found in ransomware history.
Interestingly, Threat actors behind the ransomware implemented unique features that have nowhere been found in any known ransomware.
Rorschach developed a partially autonomous that allows it to eliminate the manual actions usually performed by the other ransomware strains; instead, it automates some functions, such as creating a domain group policy (GPO).
Researchers initially found this Rorschach ransomware strain while investigating the ransomware incident in a U.S.-based company.
It was deployed using a signed component of a commercial security product, and the ransomware didn’t associate with any ransomware groups and affiliates.
Rorschach Ransomware Technical Analysis
During the behavioral analysis, as it is partially autonomous, researchers noted that the ransomware spreads itself automatically soon after it gets executed on the Domain controller and the event logs from the infected machines.
Rorschach can change the behavior based on the operator’s needs based on built-in configuration as well as numerous optional arguments.
Researchers believe that the ransomware inspired by the most infamous ransomware families also added some unique functionality, such as direct syscalls.
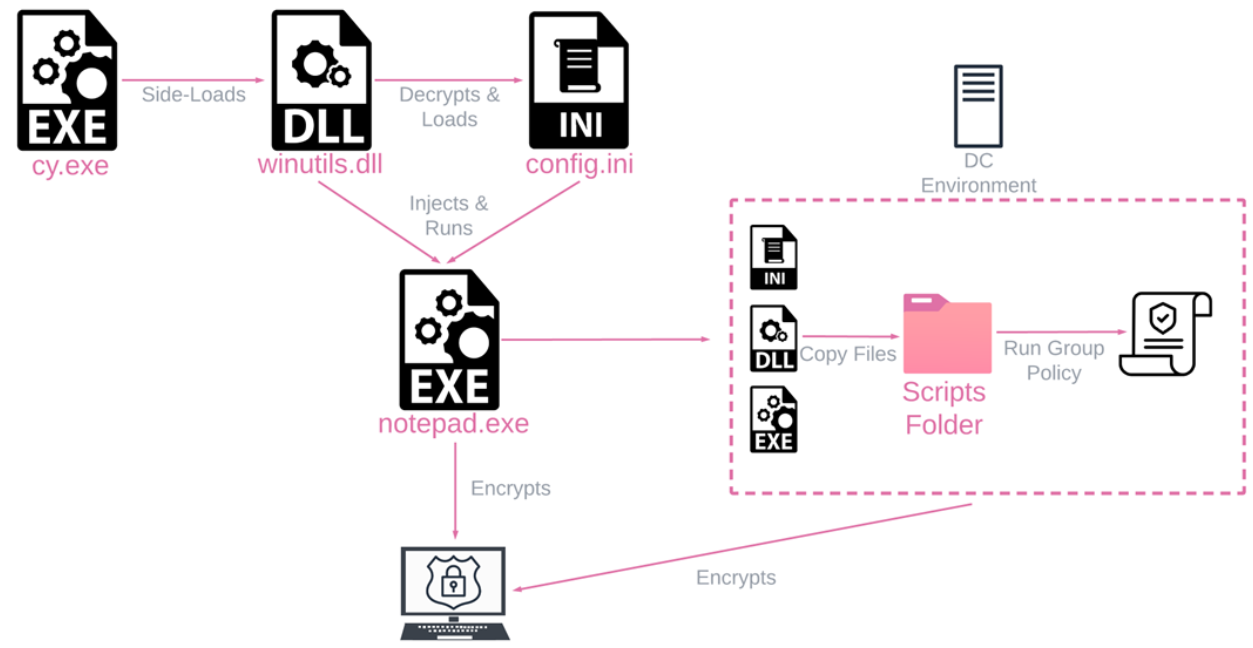
Rorschach uses Cortex XDR Dump Service Tool, a commercial security product from Palo Alto used for DLL side-loading to deploy in the targeted victim’s machine.
During the execution phases, Rorschach employed 3 files of the following:
- cy.exe – Cortex XDR Dump Service Tool version 7.3.0.16740, abused to side-load
winutils.dll - winutils.dll – Packed Rorschach loader and injector, used to decrypt and inject the ransomware.
- config.ini – Encrypted Rorschach ransomware which contains all the logic and configuration.
To make the analysis hard, Rorschach utilizes SUSPEND mode to run the spawns processes, deliver the falsified arguments, and make the execution unique by replacing it with the actual argument and rewritten in memory.
The above technique is used to perform the following operation.
- Attempt to stop a predefined list of services using
net.exe stop. - Delete shadow volumes and backups to harden recovery using legitimate Windows tools such as
vssadmin.exe,bcdedit.exe,wmic.exe, andwbadmin.exe - Run
wevutil.exeto Clear the following Windows event logs: Application, Security, System, and Windows Powershell. - Disable the Windows firewall using
netsh.exe
Rorschach is employed the unusual technique to evade defense mechanisms. Also, the ransomware automatically creates a Group Policy, spreading itself to other machines within the domain.
Encryption Process
Rorschach uses an encryption method that is a highly effective and fast hybrid cryptography scheme that is mixed of curve25519 and eSTREAM cipher hc-128 algorithms for the encryption process.
This method helps Rorschach to encrypt the specific portion of the file instead of the entire file. “The WinAPI CryptGenRandom is utilized to generate cryptographically random bytes used as a per-victim private key. The shared secret is calculated through curve25519, using both the generated private key and a hardcoded public key. ” Checkpoint said.
” Rorschach’s encryption routine suggests not only the fast encryption scheme mentioned previously but also a highly effective implementation of thread scheduling via I/O completion ports.’
As a result of the speed test, Rorschach encrypts the files within 4 minutes, 30 seconds, when LockBit v.3 took 7 minutes.
Ransom Notes
Rorschach ransomware is not clearly associated with any known ransomware group, and the ransomware note is entirely different.

According to the report, the resulting ransom note was completely different. The note was very similar to those issued by DarkSide, which probably led to this new ransomware being named “DarkSide,” despite the group being inactive since May 2021.”
IOCs
Files
| Name | Hash | Comments |
| cy.exe | 2237ec542cdcd3eb656e86e43b461cd1 | PA Cortex Dump Service Tool (benign file) |
| winutils.dll | 4a03423c77fe2c8d979caca58a64ad6c | Loader and injector into notepad.exe |
| config.ini | 6bd96d06cd7c4b084fe9346e55a81cf9 | Encrypted ransomware payload |
Building Your Malware Defense Strategy – Download Free E-Book
Read Read:
Ransomware Groups Attacking Satellite and Space Industry
ChatGPT Ready to Write Ransomware But Failed to Go Deep
Royal Ransomware Made Upto $11 Million USD Using Custom-Made Encryption Malware
Dish Network Hacked – Ransomware Attack Causes Multi-Day Outage



.png
)
