A North Korean state-sponsored threat group known as “Slow Pisces” has been orchestrating sophisticated cyberattacks targeting developers in the cryptocurrency sector using malware-laced coding challenges.
This campaign employs deceptive tactics and advanced malware techniques designed to infiltrate systems, steal critical data, and generate revenue for the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (DPRK).
Background of Slow Pisces
Also known by aliases such as Jade Sleet, TraderTraitor, and PUKCHONG, Slow Pisces has been linked to several cryptocurrency heists, netting billions of dollars in recent years.
In 2023 alone, the group reportedly stole over $1 billion, leveraging methods such as fake trading applications, supply chain compromises, and malware distributed via the Node Package Manager (NPM).
The group’s capabilities were highlighted again in 2024 when they targeted a Dubai-based cryptocurrency exchange, stealing an estimated $1.5 billion. Their activities represent a major cybersecurity threat to organizations in the cryptocurrency sector.
Campaign Strategy Overview
The Slow Pisces campaign unfolds through a three-stage process designed to exploit trust and deliver sophisticated malware payloads.
The group’s approach primarily involves impersonation on professional platforms, tailored targeting, and advanced evasion techniques.
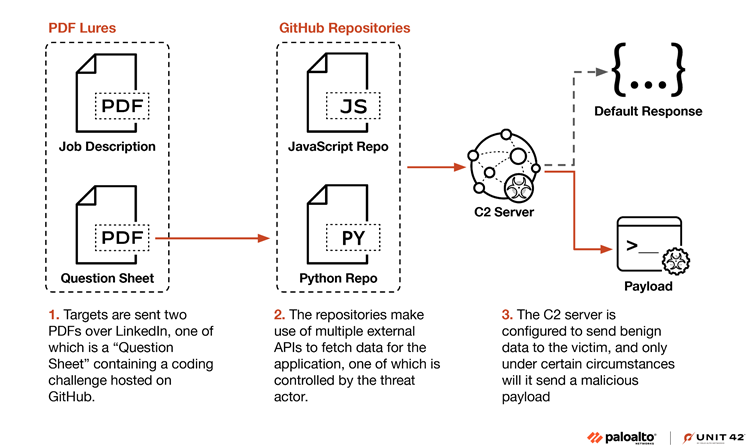
Stage 1: LinkedIn and PDF Lures
Slow Pisces begins by posing as recruiters on LinkedIn, engaging cryptocurrency developers with fake job opportunities.

They send out benign PDF documents, such as job descriptions and coding challenges.
These documents appear legitimate, often containing tasks like enhancing cryptocurrency-related projects. The challenges direct targets to GitHub repositories containing malicious code.
Stage 2: Malicious GitHub Repositories
The malicious GitHub repositories contain code adapted from legitimate open-source projects but include hidden malicious elements.
These repositories primarily cater to popular programming languages in the cryptocurrency field, such as Python and JavaScript.
The malware lies dormant until specific conditions are met, allowing the attackers to remain undetected for prolonged periods.
Python Code Techniques
The attackers use YAML deserialization in Python repositories. This inherently unsafe method, activated in specific conditions, lets the malware execute arbitrary code without raising red flags.
JavaScript Code Techniques
For JavaScript repositories, the group employs the Embedded JavaScript (EJS) templating tool. By exploiting the escapeFunction field in EJS, attackers can execute malicious code on targeted systems.
Advanced Malware Tools
RN Loader and RN Stealer
Targets who execute the malicious projects encounter two payloads: RN Loader and RN Stealer. These payloads serve distinct purposes:
- RN Loader: Collects basic system information and establishes communication with a command-and-control (C2) server.
- RN Stealer: Functions as an infostealer, capable of extracting sensitive information such as SSH keys, saved credentials, and cloud service configurations.
Both payloads are designed to operate in memory, ensuring minimal forensic footprint.
Analysis of Infrastructure and Tactics
Slow Pisces employs highly guarded C2 infrastructure that mimics legitimate domains such as Wikipedia or open-source APIs.
The group validates targets before delivering malicious payloads, ensuring that benign data is served to non-targets. These measures highlight their operational sophistication and focus on avoiding detection.
This campaign underlines the persistent risk faced by cryptocurrency developers and organizations. Slow Pisces’ advanced techniques, such as the use of YAML deserialization and EJS escapeFunction, increase the difficulty of detecting malicious actions.
Furthermore, by exploiting professional platforms like LinkedIn and GitHub, the group weaponizes trusted environments to compromise its targets.
According to Palo Alto Networks, Slow Pisces continues to refine its methods, posing significant challenges for cybersecurity professionals in 2025.
With past successes fueling continued campaigns, cryptocurrency developers and organizations must adopt proactive security measures to counter these evolving threats.
Platforms like LinkedIn and GitHub are urged to enhance their vetting processes to minimize misuse and protect their user bases.
Experts predict the group’s operations will persist, underscoring the importance of vigilance and robust cybersecurity strategies in the ongoing fight against state-sponsored cybercrime.
Find this News Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, & X to Get Instant Updates!



.png
)
