TroubleGrabber, the latest in a line of credential stealers, spreads via Discord attachments and uses Discord webhooks to hand over stolen data and information to its users.
Discord is a VoIP, IM, and distribution platform designed for creating communities, which facilitates communication via voice calls, video calls, text messaging, media, and files in private and public chat.
TroubleGrabbers bears similarity to AnarchyGrabber, another credential -stealing Trojan, though it seems to be executed differently. TroubleGrabber is written by an individual named “Itroublve” and is currently used by multiple threat actors to target Discord users.
TroubleGrabber Malware Target
TroubleGrabber arrives primarily by drive-by-download, steals the web browser tokens, Discord webhook tokens, web browser passwords, and system information. TroubleGrabber primarily targets gamers, based on the file names and delivery mechanism.
TroubleGrabber was first discovered in October 2020, when more than 5,700 public Discord attachment URLs hosting malicious content mostly in the form of Windows executable files and archives were found.
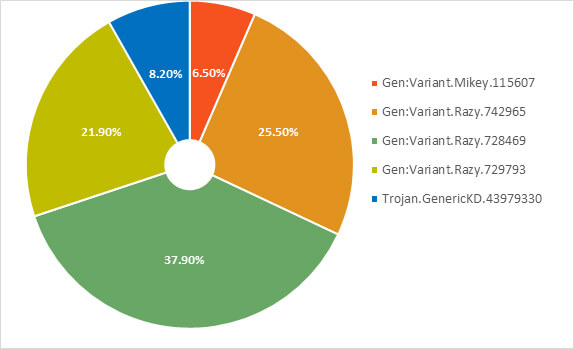
The detections are primarily related to two groups of malware namely GameHack and TroubleGrabber, with Gen:Variant.Mikey.115607 and Trojan.GenericKD.43979330 belonging to the former group, and the others to the latter.
Attack flow

- TroubleGrabber is delivered to the victim’s machine through a Discord attachment link.
- TruoubleGrabber then uses Discord and Github for downloading the next stage payloads to the victim’s machine.
- The payloads steal victims credentials like system information, IP address, web browser passwords, and tokens and sends them as a chat message back to the attacker via a webhook URL.
TroubleGrabber has similarities to different password and token stealer families, which is a malware that steals passwords and user tokens, disables two Factor Authentication, and spreads malware to the victim’s Discord server. But still, this is a completely new implementation and does not appear to be linked to the same group.
Observations
TroubleGrabber is the most recent example of malware that abuses cloud apps across every stage of the kill chain.
Here you can see the most 4 common techniques of TroubleGrabber:
- Using cloud apps for initial delivery
- Using cloud apps for next stage payload delivery
- Using cloud apps for command and control
- Stealing cloud app credentials
TroubleGrabber the new kid on the block is yet another credential-stealing malware that exploits the trust users place on the Cloud apps. Does this kid grow up or go away? Only time will tell.
You can follow us on Linkedin, Twitter, Facebook for daily Cybersecurity and hacking news updates.
Also Read
RATicate – Hackers Group Launching an Information Stealing Malware via Remote Admin Tool
FinSpy Malware Attacking iOS and Android Devices to Steal Personal Information



.png
)
