A threat actor has been identified as creating fraudulent Skype, Google Meet, and Zoom websites to distribute malware, explicitly targeting Android and Windows users.
This article delves into the details of this malicious campaign and explains how users can identify and protect themselves from these threats.
Attack Sequence:
A threat actor distributes various malware families through fake Skype, Zoom, and Google Meet websites.
Remote Access Trojans (RATs) such as SpyNote RAT for Android, NjRAT and, DCRat for Windows are being distributed.
Are you from SOC and DFIR teams? – Join With 400,000 independent Researchers
Malware analysis can be fast and simple. Just let us show you the way to:
- Interact with malware safely
- Set up virtual machine in Linux and all Windows OS versions
- Work in a team
- Get detailed reports with maximum data If you want to test all these features now with completely free access to the sandbox: ..
The attacker utilized shared web hosting with all fake sites hosted on a single IP address in Russia.
Malicious URLs closely resemble legitimate websites, making it challenging for users to differentiate.
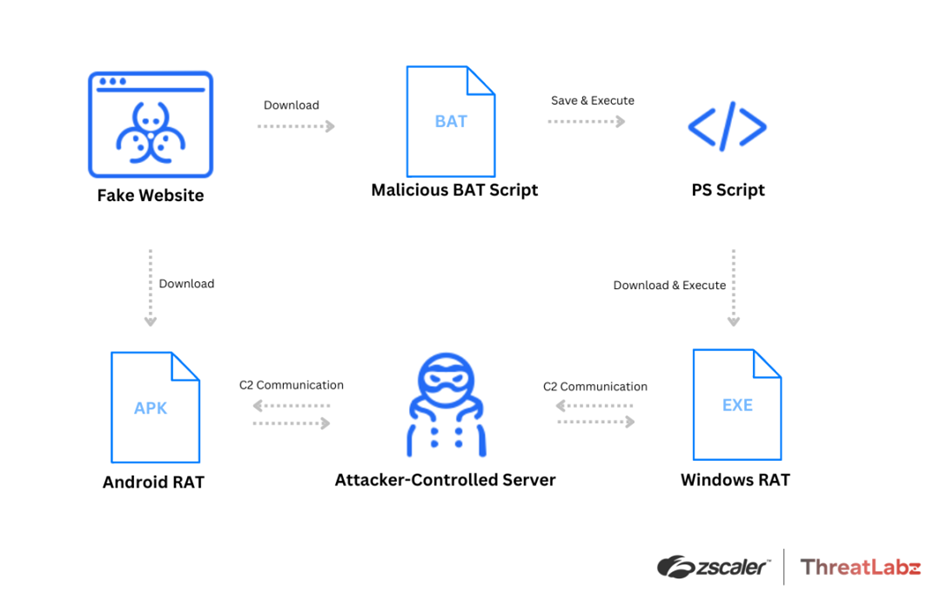
The attacker’s modus operandi involves luring users to click on fake sites where clicking on the Android button initiates the download of a malicious APK file, while clicking on the Windows button triggers the download of a BAT file, leading to a RAT payload download.
Rest assured that Zscaler’s ThreatLabz team diligently monitors and shares expert insights on all potential threats to keep you and the wider community safe.
Skype:
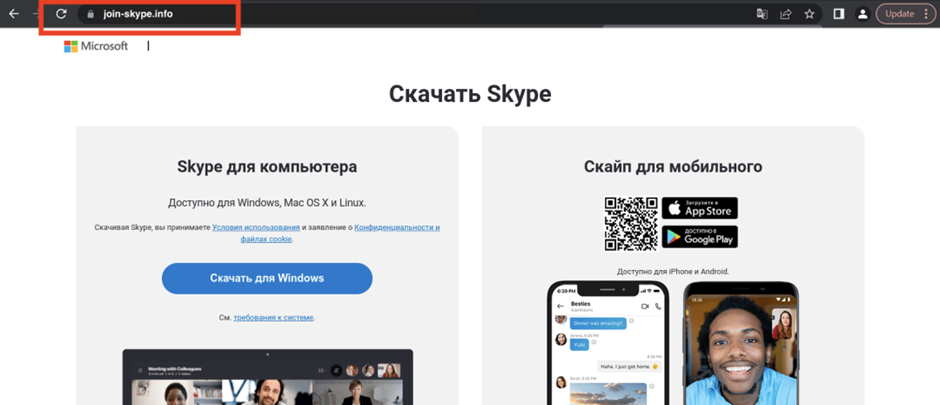
The first fake site discovered was join-skype[.]info, designed to deceive users into downloading a fake Skype application.
The Windows button is directed to Skype8.exe and the Google Play button is pointed at Skype.apk.
Google Meet:
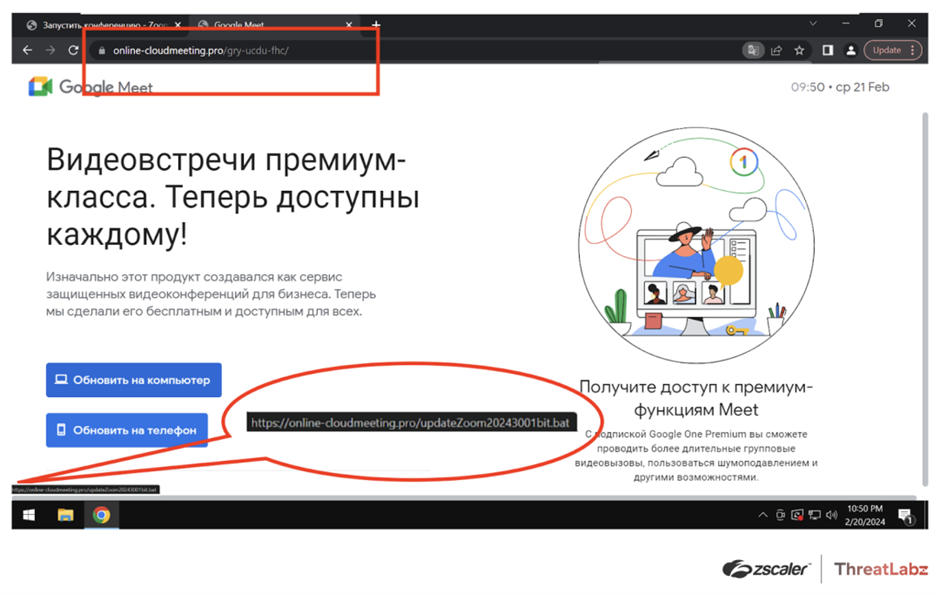
Another fake site, online-cloudmeeting[.]pro, mimicking Google Meet, was identified. The site provided links to download fake Skype applications for Android and Windows.
The Windows link led to a BAT file downloading DCRat, while the Android link led to a SpyNote RAT APK file.
Zoom:
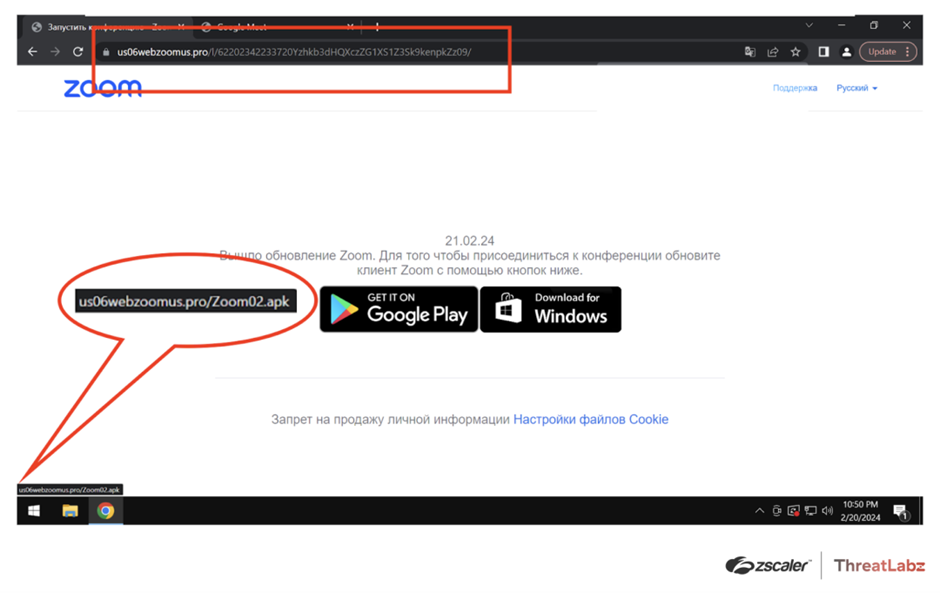
Later, a fake Zoom site, us06webzoomus[.]pro, emerged with links to download SpyNote RAT for Android and DCRat for Windows.
The site closely resembled a legitimate Zoom meeting ID.
Open Directories:
The fake Google Meet and Zoom sites also contained additional malicious files like driver.exe and meet.exe (NjRAT), indicating potential future campaigns utilizing these files.

Businesses are at risk of impersonation attacks through online meeting applications, leading to the distribution of RATs that can compromise sensitive data.
Vigilance, robust security measures, regular updates, and patches are crucial in safeguarding against evolving cyber threats. Proactive measures are essential as cyber threats evolve.
Zscaler’s ThreatLabz team remains dedicated to monitoring these threats and sharing insights with the community.
You can block malware, including Trojans, ransomware, spyware, rootkits, worms, and zero-day exploits, with Perimeter81 malware protection. All are incredibly harmful, can wreak havoc, and damage your network.
Stay updated on Cybersecurity news, Whitepapers, and Infographics. Follow us on LinkedIn & Twitter
.webp?w=696&resize=696,0&ssl=1)


.png
)
