Antivirus products continuously advance to combat evolving threats, prompting malware developers to create new bypassing techniques like “packing” and “crypting,” GuLoader is a notable service employed by cybercriminals to avoid detection by antivirus software.
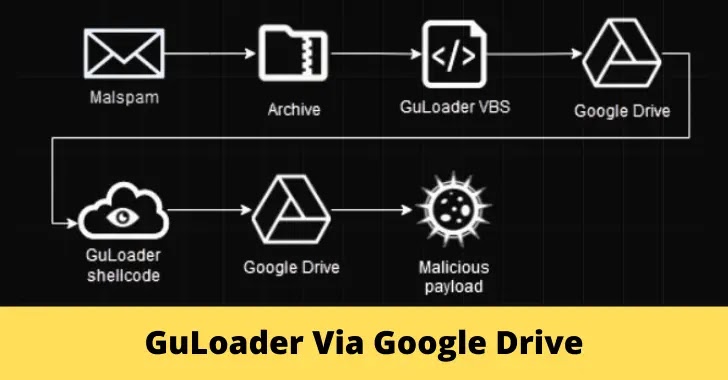
The cybersecurity researchers at Check Point affirmed that GuLoader employs a range of evasion techniques and stands out for its encrypted payload being uploaded to a remote server, enabling attackers to utilize a securely protected shellcode-based loader that downloads, decrypts, and executes the payload in memory without storing decrypted data on the hard drive.
Besides Google’s diligent attempts to impede the encrypted malicious payloads of GuLoader, most instances still witness GuLoader successfully retrieving payloads from Google Drive.

Malware Delivered using Google Drive
Conclusive evidence uncovered by researchers indicates that GuLoader is presently being employed as a distribution mechanism for the subsequent malware strains:-
- Formbook
- XLoader
- Remcos
- 404Keylogger
- Lokibot
- AgentTesla
- NanoCore
- NetWire
Earlier iterations of GuLoader were VB6 applications that utilized encrypted shellcode to handle essential tasks like loading the encrypted payload, decrypting it, and executing it from memory, while the current prevalent versions rely on:-
- VBScript
- NSIS installer

Techniques Followed by GuLoader
Both the NSIS and VBS variants of GuLoader utilize the same version of shellcode, which incorporates numerous anti-analysis techniques similar to previous versions.
Here below, we have mentioned the techniques used:-
- Sandbox evasion techniques
- Anti-debugging techniques
While previous versions of GuLoader could be bypassed using a debugger during dynamic analysis, security analysts face significant challenges in the new version due to a technique that hampers both debugging and static analysis.
Since late 2022, GuLoader’s shellcode has incorporated a novel anti-analysis method involving generating numerous exceptions that disrupt the code’s regular execution flow, with control subsequently transferred to a dynamically calculated address through a vector exception handler.
The storage method for the payload decryption key mirrors that of the encrypted strings, yet the key remains unencrypted distinctively. Typically, the key length falls within the range of 800 to 900 bytes.
To evade automated analysis, GuLoader employs a deceptive tactic by using a different size, not the one stored with the key, which poses a challenge for decryption as only the initial 843 bytes of the payload can be decrypted accurately, leaving the remaining data fragmented.
From previous versions of GuLoader, the payload decryption algorithm remains unchanged, with the initial 64 bytes of the downloaded data skipped.
GuLoader obtains the final key by assuming that the first 2 bytes of the decrypted payload are “MZ” and calculates a 2-byte XOR key (rand_key), which is used to XOR the payload decryption key.
By employing encryption, omitting headers, and separating payloads from the loader, threat actors render their malicious payloads undetectable by antiviruses, enabling them to utilize Google Drive as a storage medium and circumvent its antivirus safeguards, with some download links to these payloads persisting for extended durations.
Shut Down Phishing Attacks with Device Posture Security – Download Free E-Book





%20(1).webp)

.webp)

