A new Mac ransomware strain observed targeting macOS Users through pirated versions of popular mac software shared on popular torrent sites.
Users noted the malicious version of popular software that available for download on a Russian forum that dedicated to sharing piracy software links.
Mac ransomware
The Mac ransomware was first spotted by malware researcher Dinesh Devadoss, that piece of ransomware distributed as a Google software update program based on users commands the malware to be available since 22 June 2020.
The ransomware has zero detections with virus total, all the AV engines marked the application as safe.
Other researchers Thomas Reed, Director of Mac & Mobile at Malwarebytes, and Phil Stokes, macOS security researcher at SentinelOne also investigated the EvilQuest ransomware strain.
Reed who analyzed the malicious version of Little Snitch installer stated that “is attractively and professionally packaged, with a well-made custom installer that is properly code signed.”
The installation process, icons look like the legitimate Little Snitch installer and uninstaller apps, it also runs a shell script once installation completed.
The malware installation process is not much sophisticated, so there below the success rate with the ransomware strain.
Once the malware infection process begins it starts spreading itself around the hard drive and it also set up persistence.
Reed observed, “that files are executed as a part of GoogleSoftwareUpdate which are most commonly found installed due to having Google Chrome installed on the machine.”

Unlike other malware it is not smart enough to encrypt files alone, it also encrypts several settings files and other data files, such as the keychain files.
After infection, if a user tries to log in, it shows the following error with the keychain.

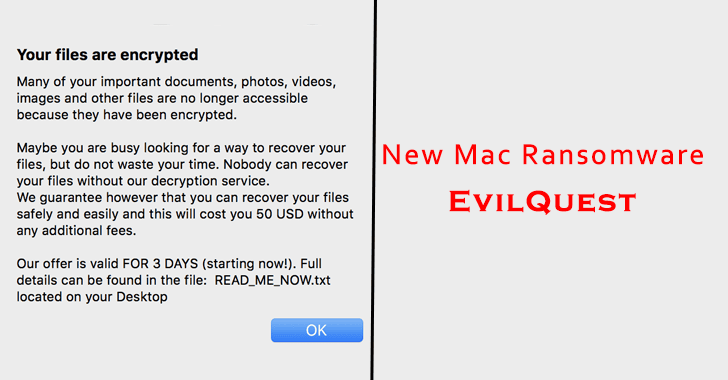
Once the encryption process completed it shows the following ransom notice.

Following are the malware capabilities
- ransoms your files
- pops a reverse shell
- steals your keystrokes
- executes in-memory payloads
The malware also includes some anti-analysis techniques, if it executed inside the virtual machine, it won’t show it’s full capabilities.
The malware armed with several capabilities allows attackers to gain full control over an infected host.
You can follow us on Linkedin, Twitter, Facebook for daily Cybersecurity and hacking news updates.
Also Read
Beware of New Mac Malware Spreading via Poisoned Google Search Results





%20(1)%20(1).webp)
.webp)


.webp)