A malware campaign targeting the Ministries of Foreign Affairs of NATO-aligned countries was recently discovered, which used PDF files masquerading as a German Embassy email. One of the PDF files consists of Duke malware which was previously linked with a Russian-state-sponsored cyber espionage group, APT29.
APT29 was attributed to Russia’s Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR) and uses Zulip, an open-source chat application for command and control. This evades and hides the malicious network traffic behind legitimate traffic.
PDF with HTML Smuggling
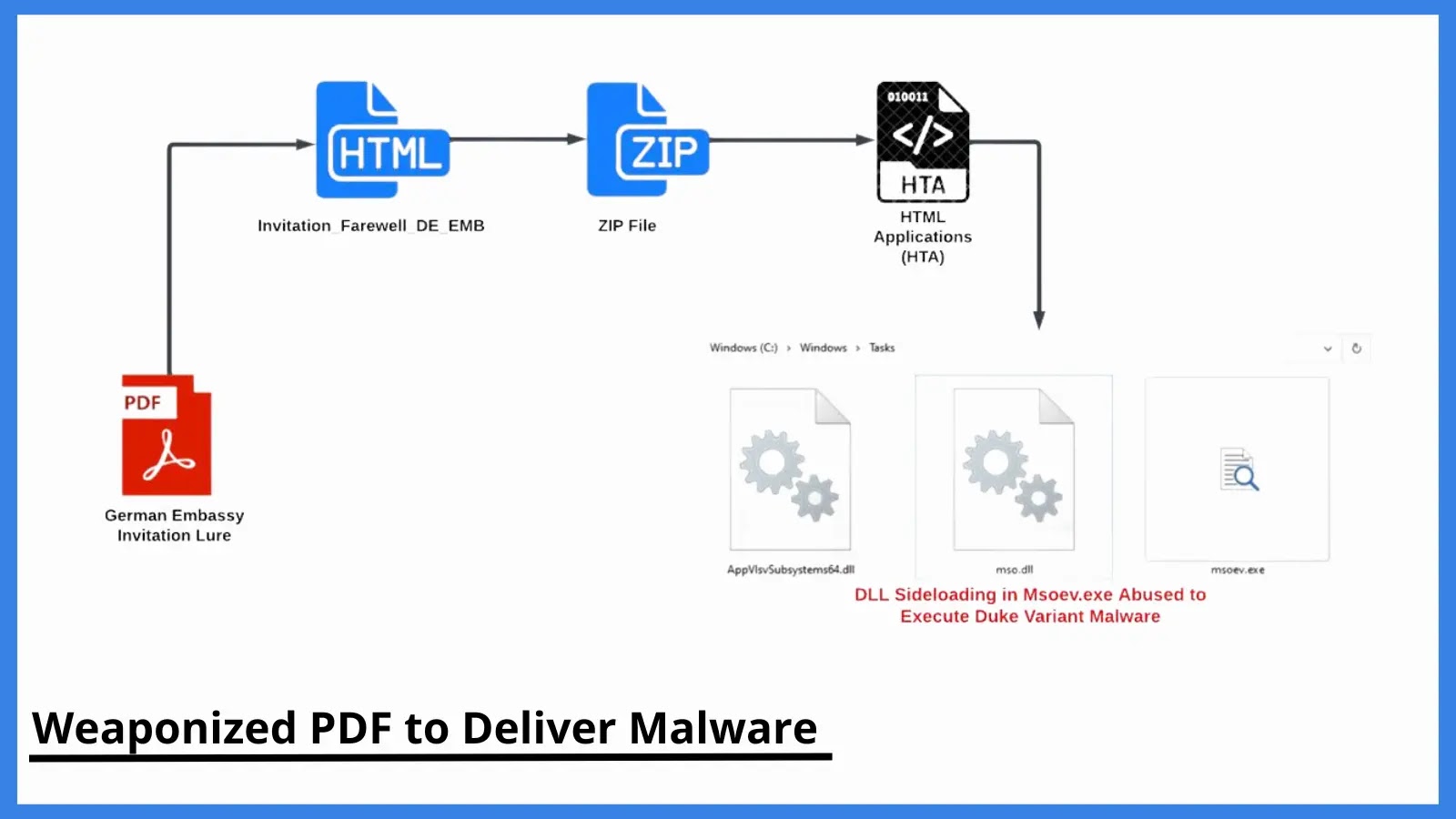
Further investigations revealed that these two PDF files that are received through email consist of an invitation lure that targets diplomatic entities. The themes used for these documents have contents related to “Farewell to Ambassador of Germany” and “Day of German Unity”.
The first PDF document also contains an embedded JavaScript code for delivering the multi-staged payloads in HTML file format. When the victim opens the file after the warning from Adobe Acrobat, the code launches the malicious HTML file called “Invitation_Farewell_DE_EMB”.
Through HTML Smuggling, a malicious HTML application file (HTA) is received, which is a widely used LOLBIN (Living Off the Land BINary). This HTA file acts as a standalone malware application that gets executed by the Windows HTA engine mshta.exe. This execution delivers the Duke malware variant.
The other PDF document does not contain any malicious contents; instead, it sends a notification to the threat actor whether the attachment was opened.
DLL Sideloading Abused to Execute Duke Variant Malware
The HTA file drops three executables on the directory C:\Windows\Tasks for DLL sideloading. The three files include
- AppVIsvSubsystems64.dll – This is a library loaded into msoev.exe for performing the execution without any failure.
- Mso.dll – This is the Duke malware variant that is loaded into the msoev.exe through DLL Sideloading.
- Msoev.exe – This is a signed Windows binary that automatically loads mso.dll and AppVIsvSubsystems64.dll when executed.
A complete report has been published, which provides detailed information on the malware campaign and the activities carried out.
Indicators of Compromise
PDF Lure:
Fc53c75289309ffb7f65a3513e7519eb
50f57a4a4bf2c4b504954a36d48c99e7
C2 Servers:
toyy[.]zulipchat[.]com
sgrhf[.]org[.]pk
edenparkweddings[.]com
Duke Malware Variant:
0be11b4f34ede748892ea49e473d82db
5e1389b494edc86e17ff1783ed6b9d37
d817f36361f7ac80aba95f98fe5d337d
MITRE ATT&CK Techniques
Spearphishing Attachment - T1566.001
DLL Side-Loading - T1574.002
HTML Smuggling - T1027.006
Embedded Payloads - T1027.009
Dynamic API Resolution - T1027.007
System Binary Proxy Execution: Mshta - T1218.005
Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols - T1071.001
User Execution: Malicious File - T1204.002
Compromise Infrastructure: Web Services - T1584.006
Keep informed about the latest Cyber Security News by following us on GoogleNews, Linkedin, Twitter, and Facebook.







%20(1).webp)
%20(1)%20(1).webp)
